
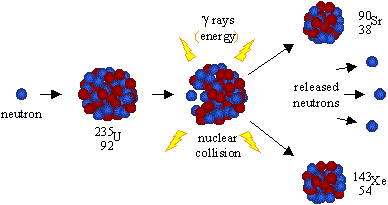
The number of protons in the nucleus, which determines the chemical properties of an element, is called the atomic number. Hence the nominal mass, based on the mass number, approximates the actual atomic mass. The nominal mass of an atom is not affected by the number of electrons, which are very light. The nominal mass of an atom of an element is measured by the sum of the protons and neutrons in it. The energy balance in the decay of a neutron is achieved by theĪnti-neutrino, a neutral particle that carries off surplus energy as the Protons are about 1,836 times heavier than electrons, and neutrons are about 1,838 times heavier than electrons. However, it is remarkable that neutrons, when they exist together with protons in the nucleus of atoms, are stable. Neutron => proton + electron + antineutrino

The mass of an atom lies almost entirely in its nucleus since protons and neutrons are far heavier than electrons.įree neutrons are unstable particles which decay naturally into a proton and electron, with a half-life of about 12 minutes. As a result, atoms of elements are normally electrically neutral. The number of electrons in an atom is normally equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. Electrons are electrically negative and have a charge equal in magnitude to that of a proton. The nuclei of atoms are composed of protons, which have a positive electrical charge, and neutrons, which are electrically neutral. The atoms of which every element of matter is composed have a nucleus at the center and electrons whirling about this nucleus that can be visualized as planets circling around a sun, though it is impossible to locate them precisely within the atom. Some of the terms used in this factsheet can be found in IEER’s on-line glossary.

Is the sun an example of fission?Īlthough the energy produced by fission is comparable to what is produced by fusion the core of the sun is dominated by hydrogen and at temperatures where hydrogen fusion is possible so that the dominant source of energy per cubic meter is in fusion rather then the fission of very low abundance radioisotopes.A basic background in nuclear physics for those who want to start at the beginning. … The outward pressure from the fusion reactions keeps the stars from collapsing. Nuclear fusion the source of all the energy so generously radiated by the Sun does two things: it converts hydrogen into helium (or rather makes helium nuclei from protons) and it converts mass to energy. How does nuclear fusion in the Sun create energy? … The mass of a Helium nucleus is 0.7% smaller than the mass of four protons (Hydrogen nuclei). Explanation: High temperatures enable nuclear fusion to happen in the core. The Sun releases energy by fusing four hydrogen nuclei into one helium nucleus. Fusion occurs when protons of hydrogen atoms violently collide in the sun’s core and fuse to create a helium atom. Solar energy is created by nuclear fusion that takes place in the sun. Solar energy is any type of energy generated by the sun. The material in the center of the disk became denser and hotter and started to form a star and began to spin faster. When did the sun form quizlet?Ĥ.6 billion years ago like every star the sun formed from a cloud of dust and gas. Its name is derived from the way energy is carried outward through this layer carried by photons as thermal radiation. Moving outward next comes the radiative (or radiation) zone. It the hottest region where the nuclear fusion reactions that power the Sun occur. In which layer of the sun does nuclear fusion occur?
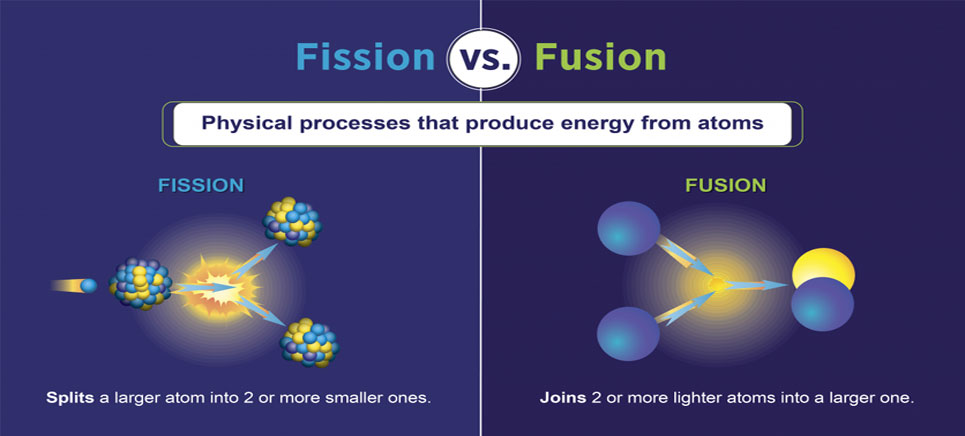
The sun’s surface is about 6 000 Kelvin which is 10 340 degrees Fahrenheit (5 726 degrees Celsius). Nuclear fusion creates heat and photons (light). The core of the sun is so hot and there is so much pressure nuclear fusion takes place: hydrogen is changed to helium. Which is responsible for producing heat and light from the sun?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
